SQL Triggers
Topics on this page
What & Why of Triggers
Triggers are objects that are stored in the database, that execute when they are triggered by a specific DML statement.
For example, we could create a trigger that is associated with an INSERT operation on the Staff table. Every time we execute an INSERT on the Staff table, the code in that trigger will execute.
Triggers cannot be explicitly executed, and cannot accept parameters.
Triggers can help us to
- Enforce referential integrity across databases
- Enforce business rules (too complex for
CKconstraint) - Automate an operation (backup, archive)
- Create an audit trail
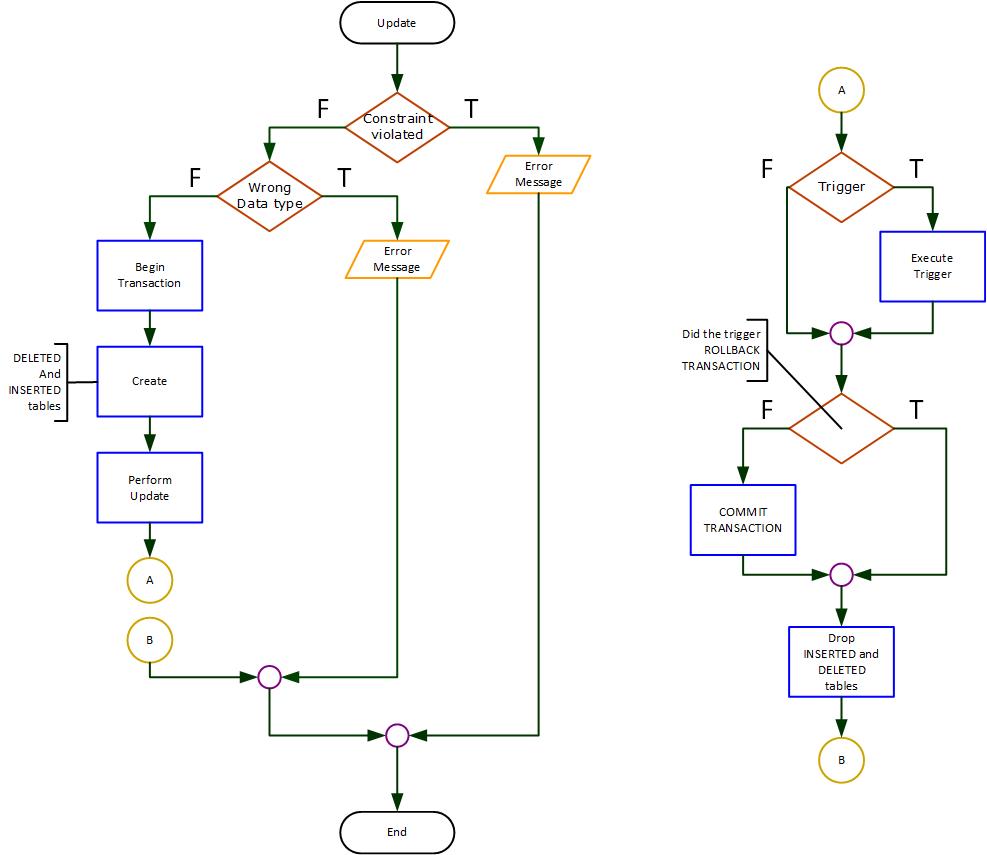
Temporary Tables
Two temporary tables are created and used by the server when executing a DML operation.
DELETED: contains the before image of all rows affectedINSERTED: contains the after image of all rows affected
We will use the term “base table” to refer to the table the trigger is associated with.
Temporary tables for INSERT
If the trigger is associated with an INSERT on the base table:
INSERTEDcontains the new rowsDELETEDis empty- Base table contains the new rows and all previously existing rows
Temporary tables for a DELETE
If the trigger is associated with a DELETE on the base table:
DELETEDcontains the deleted rowsINSERTEDis empty- Base table contains all the rows that were not deleted.
Temporary tables for UPDATE
If the trigger is associated with an UPDATE on the base table:
DELETEDcontains the before image of the changed rowsINSERTEDcontains the after image of the changed rows- Base table contains the after image of the changed rows and all other rows not affected by the operation.
Trigger Execution
When can a trigger execute?
- When the DML operation affects zero rows in the base table
- When the DML operation affects one row in the base table
- When the DML operation affects many rows in the base table
The logic must work in all three conditions.
Trigger Syntax
Syntax:
CREATE TRIGGER TriggerName
ON TableName FOR [UPDATE][,] [INSERT][,] [DELETE]
AS
-- SQL statements go here
RETURN
Examples:
To create a trigger for the INSERT and UPDATE operations associated with the Staff table:
CREATE TRIGGER TR_Staff_Insert_Update
ON Staff FOR INSERT, UPDATE
AS
-- SQL statements go here
RETURN
To create a trigger for the DELETE operation associated with the Student table:
CREATE TRIGGER TR_Student_Delete
ON Student FOR DELETE
AS
-- SQL statements go here
RETURN
More Syntax
DROP TRIGGER TriggerName
ALTER TRIGGER TriggerName
ON TableName FOR [UPDATE][,] [INSERT][,] [DELETE]
AS
-- SQL statements
RETURN
Considerations
Dropping Tables
If you drop a table that has triggers associated with it, the triggers are dropped as well.
Triggers cannot exist without the table it is associated with.
Viewing Triggers
To see a list of triggers in your database:
SELECT Name
FROM SysObjects
WHERE Type = 'TR'
To see the source code of a trigger:
EXEC SP_HELPTEXT TriggerName
Practice
Practice Q #1 - How to test
To test:
- Issue an update to the
BalanceOwingcolumn that violates the data type of the column being updated. - Issue a valid update to the character wages that affects one row.
- Issue a valid update to the character wages that affects multiple rows.
- Issue a valid update to the character wages that affects zero rows
MovieCharacter ERD:
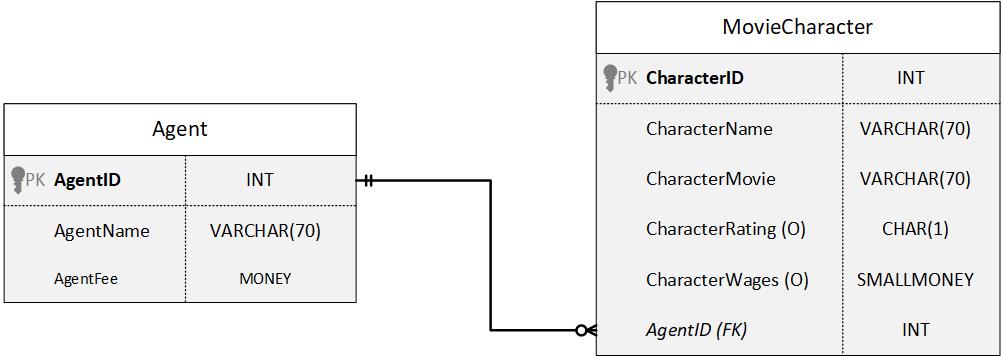
Practice Q #2
Create a trigger to enforce a rule that CharacterWages must be >= 0.
Practice Q #3
Create a trigger that enforces a rule that an AgentFee cannot be increased by more than 100% in one update.
e.g., if the AgentFee was $100, I cannot update it to a value greater than $200.
Practice Q #4
Create a trigger that enforces a rule that a MovieCharacter cannot be deleted if their Agent’s AgentFee is >= 50.
Practice Q #5
Create a trigger that enforces a rule that an Agent cannot represent more than 2 movie characters.
Practice Q #6
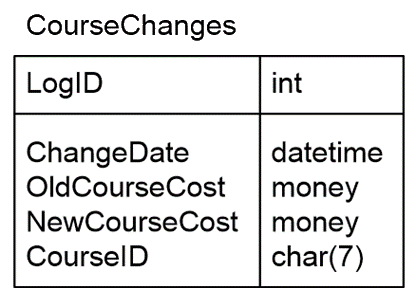
Create a trigger to Log when changes are made to the CourseCost in the Course table. The changes will be inserted in to the following Logging table:
CREATE TABLE CourseChanges(
LogID INT IDENTITY(1,1) NOT NULL
CONSTRAINT PK_CourseChanges PRIMARY KEY CLUSTERED,
ChangeDate DATETIME NOT NULL,
OldCourseCost MONEY NOT NULL,
NewCourseCost MONEY NOT NULL,
CourseID CHAR(7) NOT NULL
)
Practice Q #7
Create a trigger to enforce referential integrity between the Agent and MovieCharacter table.